Currently Empty: $ 0.00
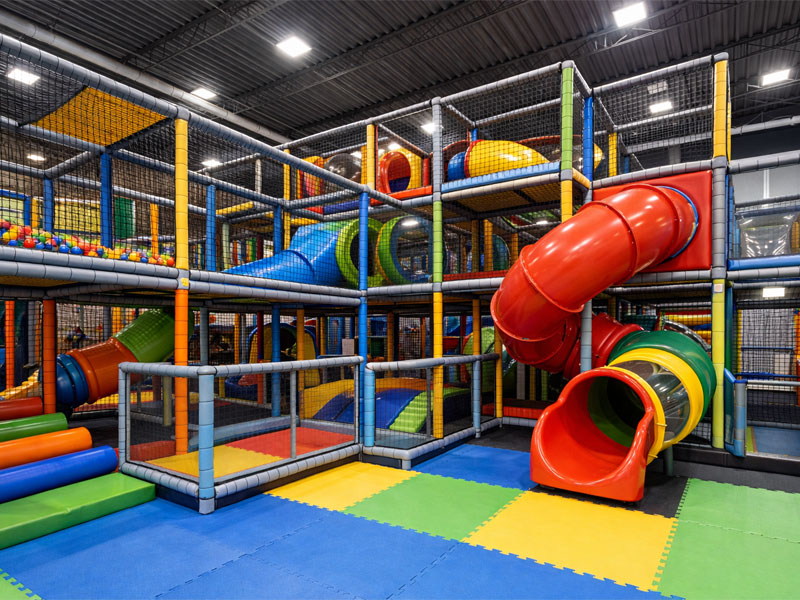

Indoor playground equipment safety standards play a critical role in the design, manufacturing, installation, and operation of commercial indoor play centers. Whether the project is a family entertainment center (FEC), shopping mall play zone, daycare facility, or trampoline park, compliance with recognized safety standards ensures child protection, liability control, and long-term operational stability.
This guide explains indoor playground equipment safety standards in practical terms, covering major international regulations, testing requirements, material safety, installation protocols, and ongoing compliance responsibilities.
Why Indoor Playground Equipment Safety Standards Matter
Indoor playgrounds are high-traffic, high-energy environments. Unlike traditional outdoor playgrounds, they often include:
- Multi-level soft play structures
- Enclosed climbing systems
- Slides and tunnels
- Foam pits
- Obstacle courses
- Trampoline integration
Because of the complexity and multi-user interaction, indoor playground equipment safety standards establish uniform design rules to reduce injury risk and structural failure.
Compliance is not optional in commercial environments—it directly affects insurance approval, inspection clearance, and operational licensing.
Main Indoor Playground Equipment Safety Standards
Safety standards vary by region. Commercial operators targeting Europe and North America must understand the relevant frameworks.
EN 1176 – European Playground Equipment Standard
EN 1176 applies to playground equipment in Europe, including indoor installations.
It covers:
- Structural integrity
- Fall height limits
- Entrapment prevention
- Material requirements
- Installation and inspection protocols
For indoor playground equipment safety standards compliance in Europe, EN 1176 certification is typically required.
ASTM F1487 – U.S. Playground Equipment Standard
ASTM F1487 is the primary standard in the United States for public playground safety.
It regulates:
- Head and limb entrapment zones
- Guardrails and barriers
- Protrusion hazards
- Performance testing
Commercial indoor playground operators in North America often rely on ASTM compliance combined with local building codes.
ASTM F1918 – Soft Contained Play Equipment
For indoor soft play structures specifically, ASTM F1918 is particularly relevant.
This standard addresses:
- Soft-contained multi-level structures
- Padding thickness
- Netting strength
- Impact attenuation
- Maintenance requirements
It is one of the most critical standards for indoor playground equipment safety in commercial environments.
EN 14960 – Inflatable Play Equipment
If inflatable elements are included in the indoor playground, EN 14960 governs:
- Anchorage
- Blower systems
- Material durability
- User capacity
Core Safety Design Requirements
Indoor playground equipment safety standards define technical design principles that manufacturers must follow.
Fall Height and Impact Attenuation
Although indoor playgrounds use padded flooring, fall height remains a regulated factor.
Standards specify:
- Maximum free fall height
- Required impact-absorbing materials
- Test methods for shock absorption
Impact attenuation testing ensures flooring reduces injury risk.
Entrapment Prevention
Entrapment is a major safety concern.
Standards define:
- Maximum and minimum openings
- Head and neck entrapment probes
- Finger entrapment tolerances
Designers must eliminate dangerous gaps in climbing nets, barriers, and panels.
Guardrails and Protective Barriers
Elevated platforms must include:
- Guardrails for specific height ranges
- Fully enclosed barriers at higher levels
- Minimum panel height specifications
Barrier design varies depending on user age group.
Structural Stability and Load Testing
Indoor playground structures must withstand:
- Dynamic loading from multiple children
- Lateral movement
- Repeated stress cycles
Manufacturers perform structural load testing to verify compliance with indoor playground equipment safety standards.
Material Safety Requirements
Material selection is critical for indoor safety compliance.
Steel and Structural Components
Structural frames are typically constructed from:
- Galvanized steel
- Powder-coated steel
Materials must resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity over time.
Padding and Soft Covering
Soft play equipment uses:
- High-density foam
- PVC or PU protective coverings
- Fire-retardant materials
Fire safety compliance is particularly important in indoor commercial spaces.
Netting and Rope Systems
Netting must meet tensile strength requirements to prevent tearing or failure under load.
Fire Safety Compliance
Indoor playground equipment safety standards intersect with local fire codes.
Requirements may include:
- Flame-retardant materials
- Smoke emission testing
- Clear emergency exit pathways
- Maximum occupancy limits
Compliance ensures operational approval and reduces liability risk.
Installation and Site Compliance
Even certified equipment can fail inspection if installed incorrectly.
Professional Installation
Installation must follow manufacturer guidelines, including:
- Anchor placement
- Structural alignment
- Proper tensioning of nets
- Securing of padding
Improper installation voids compliance.
Clearance Zones
Indoor playground equipment safety standards require adequate spacing between components to prevent collision hazards.
Inspection Before Operation
Before opening, operators should conduct:
- Structural inspection
- Safety gap verification
- Padding checks
- Documentation review
Third-party inspection may be required depending on jurisdiction.
Ongoing Inspection and Maintenance
Compliance is not a one-time event.
Indoor playground equipment safety standards require:
- Daily visual inspections
- Monthly detailed inspections
- Annual structural audits
Maintenance documentation is critical for insurance and liability protection.
Age Group Considerations
Different age groups require different safety design criteria.
- Toddler zones require lower fall heights and smaller openings.
- General play zones for ages 5–12 allow higher structures with stricter barriers.
Clear zoning improves safety compliance.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Analysis
Professional manufacturers conduct risk assessments during design.
This includes:
- Identifying foreseeable misuse
- Evaluating structural stress
- Minimizing sharp edges or protrusions
Risk analysis is a key component of modern indoor playground equipment safety standards.
Insurance and Liability Implications
Insurance providers typically require:
- Documented compliance with recognized standards
- Installation certification
- Maintenance records
Failure to comply can increase liability exposure.
How to Choose a Compliant Indoor Playground Equipment Manufacturer
When selecting a supplier, verify:
- EN 1176 / ASTM compliance documentation
- Material fire safety certifications
- Engineering drawings and load calculations
- Inspection support services
An experienced manufacturer understands regulatory requirements across different markets.
Common Compliance Mistakes
Frequent issues in indoor playground projects include:
- Mixing components from different suppliers
- Ignoring local building codes
- Failing to document inspections
- Overlooking occupancy limits
Avoiding these mistakes protects long-term operations.
Conclusion
Indoor playground equipment safety standards are essential for ensuring safe, compliant, and sustainable commercial play environments. From structural integrity and fall protection to fire safety and entrapment prevention, these standards provide a comprehensive framework for manufacturers and operators.
Understanding and implementing indoor playground equipment safety standards reduces risk, improves user confidence, and supports long-term business success.